The Evolution of Ethereum: Understanding the Halving Reason
Ethereum, one of the most popular cryptocurrencies in the market, has been on an incredible journey since its inception. The underlying technology behind this digital asset is based on a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, which requires energy and computational power to validate transactions and create new blocks. One of the key features that set Ethereum apart from other cryptocurrencies is the halving mechanism.
In this article, we will delve into the reason behind the halving reward reduction, explore its technical aspects, and discuss whether it’s purely ideological or if there are underlying technical reasons.
What is the Halving Reward?
The halving reward refers to a reduction in the number of new Ethereum blocks that can be mined per day. This mechanism aims to slow down the rate at which new coins are introduced into circulation, thereby reducing inflation and increasing the scarcity of Ether (ETH), the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum network.
Why Halve?
The halving reward is implemented as a deliberate strategy to achieve several goals:
- Inflation Control: By reducing the supply of ETH, the halving mechanism helps prevent price bubbles from forming. As more coins are removed from circulation, the total value of existing ETH increases.
- Increased Difficulty: The reduced number of new blocks per day makes it more difficult for miners to create new coins, thereby increasing the overall difficulty level in mining Ethereum.
- Improved Consensus: The halving mechanism helps maintain a consistent and fair consensus among all nodes on the network, ensuring that transactions are verified correctly.
Technical Aspects
From a technical perspective, the halving reward is implemented using a simple yet robust algorithm:
- Block Reward: Each block rewards miners with 2^7 ETH (128 ETH per block) for successfully validating and including their transaction in the block.
- Halving Factor: The number of blocks that can be mined per day is reduced by a factor of 8 every four years, or approximately every two years.
This reduction in mining difficulty is achieved through a combination of increased network hash power requirements and adjusted block rewards.
Is it purely Ideological?
While the halving reward has been implemented as a deliberate strategy to achieve specific goals, its implementation can be viewed from both technical and ideological perspectives.
From an
ideological standpoint, the halving mechanism is designed to promote responsible and sustainable growth in the Ethereum ecosystem. By reducing inflation and increasing scarcity, it helps maintain the long-term value of ETH and ensures that the network continues to support various decentralized applications (dApps) and use cases.
However, some critics argue that the halving mechanism could lead to:
- Inefficient Energy Consumption: The increased difficulty level in mining Ethereum may require significant computational power, which can consume large amounts of energy.
- Price Volatility: The halving mechanism’s impact on price can be unpredictable and volatile, leading to sudden changes in ETH’s value.
Conclusion
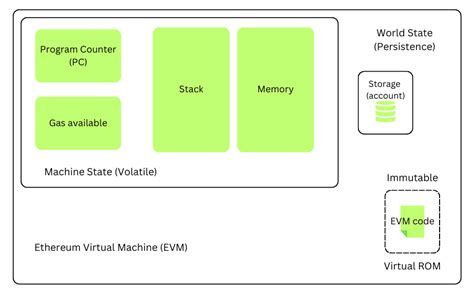
The halving reward is an essential feature that has shaped the evolution of Ethereum. While its implementation may have both technical and ideological aspects, it serves as a deliberate strategy to promote responsible growth in the network and maintain its long-term value. As the cryptocurrency landscape continues to evolve, understanding the underlying mechanisms behind the halving reward will become increasingly important for developers, investors, and users alike.
References
- Ethereum Whitepaper (2014)
- Ethereum Core Development Team (2022). [Ethereum.org](
- CryptoSlate.
